BIM quality assurance
BIM quality assurance includes not only pure model testing, but also the interpretation of the test results. The aims of BIM quality assurance are to identify and solve problems at an early stage, ensure model quality, check compliance with the specifications in the BIM rules and regulations and assess the current model status.
For the model check, the specialist models of the various specialist planners are merged into a coordination model in the quality assurance software (e.g. Solibri) and then checked. A great deal of experience in the field of classification, rule creation and model checking itself is required to carry out a comprehensive model check.
It does not make sense to use the standard rule sets without a concept or adaptations.
BIM quality assurance not only includes pure model checking, but also the interpretation of the check results. The aims of BIM quality assurance are to identify and resolve problems at an early stage, ensure model quality, check compliance with the specifications in the BIM rules and regulations and assess the current model status.
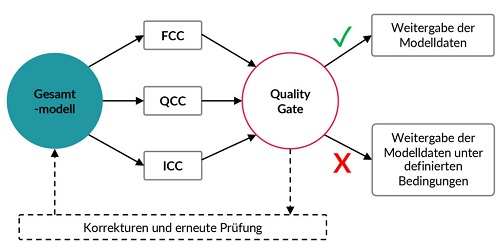
There are four main categories of checking rules introduced by the ODE:
- FCC: Formal criteria check, e.g. LOI check
- QCC: Quality criteria check, e.g. collision check
- ICC: Integrity criteria check, e.g. accessibility check
- MCC: Model comparison check, e.g. comparison of old status ARC model vs. latest status ARC model
For the test reports, it is important that they are not simply a list of the BCF slides, as this does not provide a qualitative statement on the status of the models. Test reports must clearly show whether the quality gates defined in the BIM rules and regulations have been achieved and what the current status and development of the models looks like.
The combination of an experienced model inspector, proven inspection routines and meaningful inspection reports provides an optimal setting for the execution of a successful BIM project.
Text source: ODE
Image source: BIMcert manual